
Muscle or Ligament Strain and Back Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Back pain is a pervasive issue that affects people of all ages and lifestyles. One of the most common culprits behind back pain is muscle or ligament strain. Understanding how these strains occur, their symptoms, and how they can be treated is essential for managing and preventing back pain effectively.
Causes of Muscle or Ligament Strain
Muscle or ligament strains in the back occur when the muscles or ligaments are stretched or torn. Several factors can lead to such strains, including:
1. Improper Lifting: Lifting heavy objects without using proper techniques can strain the muscles and ligaments in the back.
2. Sudden Movements: Jerky, awkward movements can cause the muscles or ligaments to stretch beyond their normal range.
3. Overexertion: Engaging in intense physical activities, especially without proper conditioning, can lead to overuse and strain.
4. Poor Posture: Prolonged periods of poor posture, whether sitting, standing, or sleeping, can place undue stress on the back muscles and ligaments.
5. Repetitive Motions: Repeating the same motions, particularly if they involve twisting or bending, can cause gradual wear and tear, leading to strain.
Symptoms of Muscle or Ligament Strain
The symptoms of muscle or ligament strain can vary in intensity, but they generally include:
• Localized Pain: A specific area of the back will often feel sore or tender. The pain can be sharp or a constant, dull ache.
• Stiffness: The affected muscles may feel tight, reducing the range of motion.
• Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions of the back muscles can occur, causing sudden and intense pain.
• Swelling and Bruising: In some cases, visible swelling or bruising may appear over the affected area.
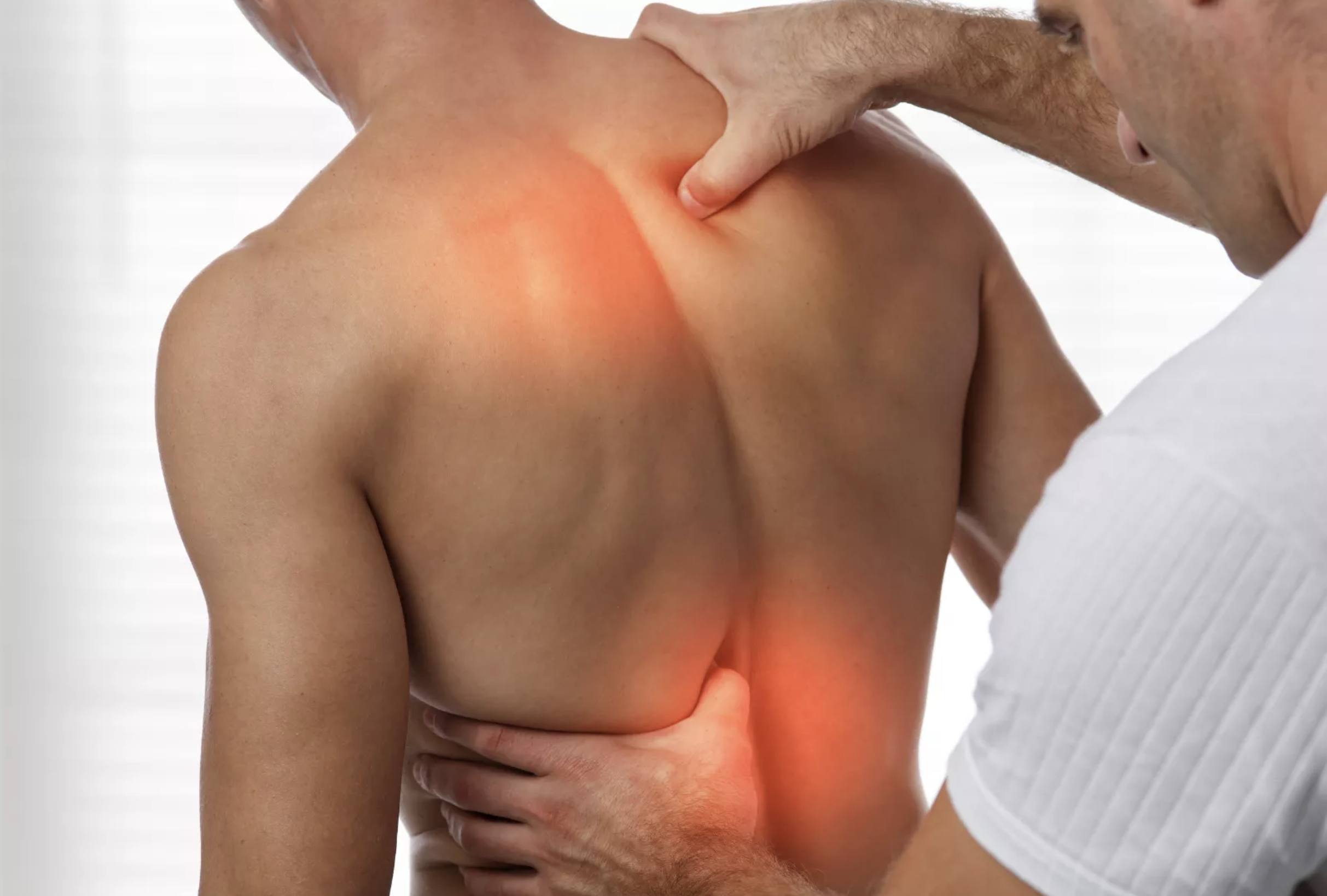
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a muscle or ligament strain typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may ask about recent activities, the onset of pain, and any previous back issues. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, are usually not necessary unless the doctor suspects a more serious condition.
Treatment
Treatment for muscle or ligament strain aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and restore mobility. Common treatment approaches include:
1. Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain allows the muscles and ligaments to heal.
2. Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs in the first 48 hours can reduce swelling and numb the pain. After that, heat packs can help relax tense muscles.
3. Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
4. Physical Therapy: Guided exercises and stretches can strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
5. Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can increase blood flow to the affected area and reduce muscle tension.
6. Supportive Devices: Using braces or supports can help stabilize the back and prevent further strain during the healing process.
Prevention
Preventing muscle or ligament strains involves adopting healthy habits and practices, such as:
• Proper Lifting Techniques: Always bend at the knees and keep the back straight when lifting heavy objects.
• Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility, reducing the risk of strain.
• Ergonomic Workspaces: Ensuring that workstations are set up to promote good posture can help prevent strain. This includes using supportive chairs and adjusting the height of desks and computer screens.
• Stretching and Warm-Up: Performing stretching exercises and warming up before physical activities can prepare the muscles and prevent strain.
• Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can place additional stress on the back muscles and ligaments.
Conclusion
Muscle or ligament strains are a common cause of back pain, often resulting from improper lifting, sudden movements, overexertion, poor posture, or repetitive motions. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment can alleviate pain and promote recovery. By adopting preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing these painful strains and maintain a healthier back. If back pain persists or is severe, it is important to seek medical advice to rule out other potential causes and receive proper care.
Eget faucibus tellus. Eget netus nec magnis fermentum. Diam quam quam suspendisse vitae consequat phasellus non odio morbi bibendum odio libero.